

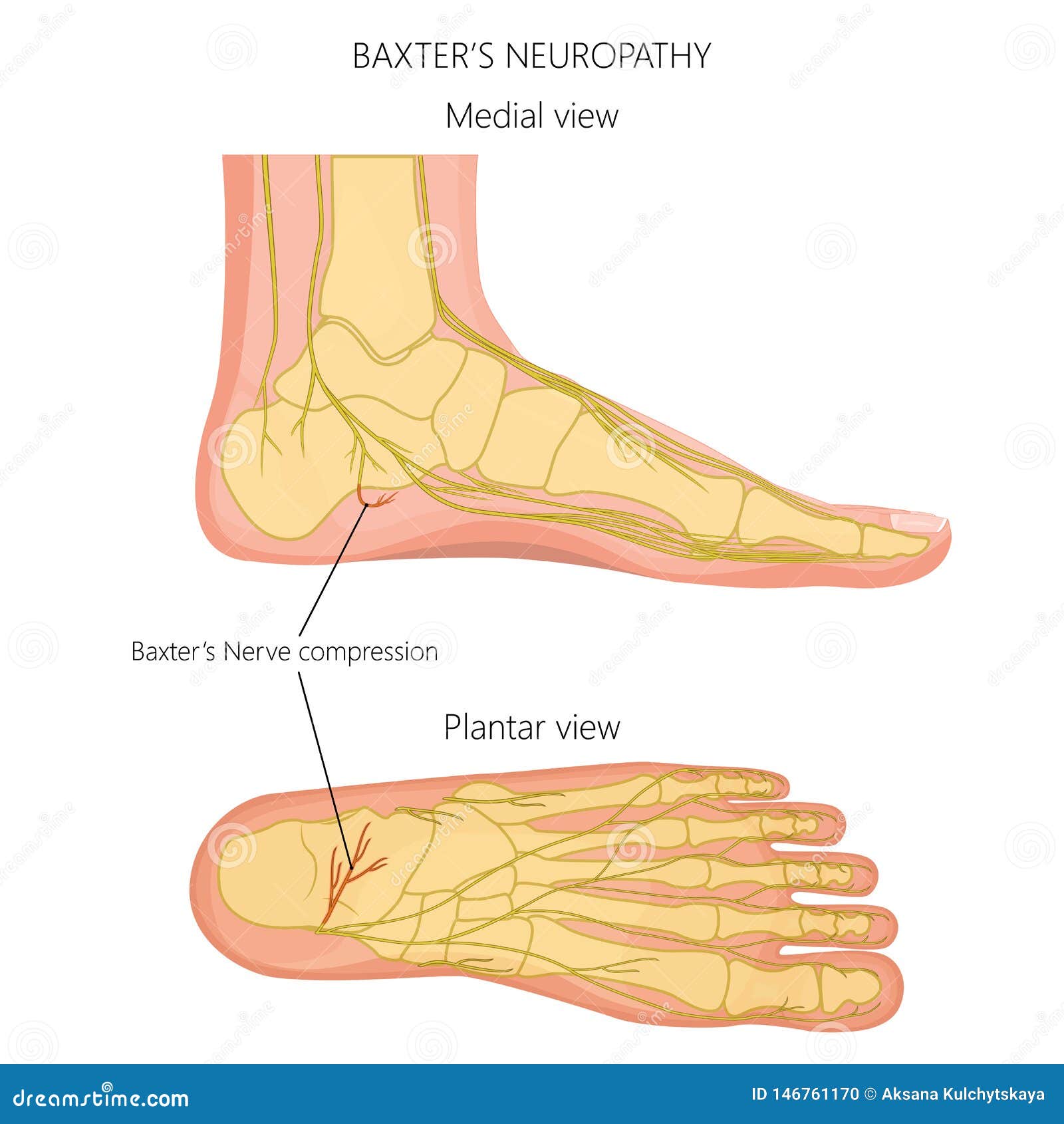
This anatomy makes the posterior aspect of the medial malleolus an excellent landmark for visualizing the tibial nerve on MR imaging where it is visible between the flexor digitorum longus and flexor hallucis longus muscle tendons. Proximal to the tip of the medial malleolus, the tibial nerve bifurcates into the medial and lateral plantar nerves at the level of the tarsal tunnel with some variation. The tibial nerve arises in the popliteal fossa as the other branch of the sciatic nerve and supplies the motor innervation to the posterior deep flexor compartment of the lower leg. The region where the extensor hallucis brevis tendon crosses over the medial branch also serves as an excellent landmark for identification of the deep fibular nerve in the foot. Regardless of variation, the anterior tibial artery makes an excellent landmark for identifying the deep fibular nerve in the leg on MR imaging. It is important to note that although the deep fibular nerve usually courses laterally to the anterior tibial artery, some anatomical variations exist.
The medial branch courses medially on the dorsum of the foot, laterally to the dorsalis pedis artery, and inferiorly to the extensor hallucis brevis tendon as it moves towards the first dorsal web space to supply its sensory innervation. The lateral branch courses deep to the extensor digitorum brevis and extensor digitorum hallucis muscles and provides their motor innervations and some sensory innervation to the ankle. At approximately 1.3 cm above the ankle joint, the nerve divides into a lateral branch and a medial branch. The deep fibular nerve descends lateral to the anterior tibial artery and is located just anterior to the interosseous membrane within the anterior compartment of the leg. The remaining portion of the superficial fibular nerve in the foot is purely sensory as it supplies sensory information to the dorsal aspect of the foot, except for the first dorsal web space. As it arises in the foot and travels more inferiorly, the superficial fibular nerve further divides into two branches: medial and intermediate dorsal cutaneous nerves, which may be subject to anatomic variation. Within the lateral compartment, the superficial fibular nerve courses within the peroneus longus muscle and emerges through the anterolateral aspect of the musculature about 12 cm above the ankle joint at the level of a defect in the deep (crural) fascia. The superficial fibular nerve supplies the motor innervation to the lateral compartment of the leg, which is responsible for foot eversion, while the deep fibular nerve supplies the motor innervation to the anterior compartment, responsible for ankle dorsiflexion, toe extension, and foot inversion. The common fibular nerve bifurcates into the superficial and deep fibular nerves. Both nerves contribute significant terminal branches that will eventually supply the foot. The common fibular nerve continues distally into the anterior and lateral compartments of the leg and foot whereas the tibial nerve descends towards the posterior compartment. The sciatic nerve, which provides motor innervation to the muscles of the posterior thigh and sensory innervation to the lateral side of the lower leg and lateral side and sole of the foot, ends just above the posterior knee in the popliteal fossa and bifurcates into the common fibular and tibial nerves. March 22, 2021.The foot nerves originate from the sciatic nerve, made up of the L4 to S3 nerve roots. Evaluation and diagnosis of common causes of forefoot pain in adults. Treating Morton's neuroma by injection, neurolysis, or neurectomy: A systematic review and meta-analysis of pain and satisfaction outcomes. In: Essentials of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation: Musculoskeletal Disorders, Pain, and Rehabilitation. American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
